你所不知道的C語言: linked list 和非連續記憶體操作
Copyright (慣C) 2018 宅色夫
- 請透過 gitter (線上對話服務,可透過 GitHub 或 Twitter 帳號登入) 提交疑問和建議事項: guts-general (按下去就對了) :::
從 Linux 核心的藝術談起
- Linus Torvalds 在 TED 2016 的訪談
 「我不是願景家,我是工程師。我對那些四處遊蕩、望著雲端的人沒有任何意見。但是我是看著地面的人,我想修補就在我面前的坑洞,以免跌進去。」
「我不是願景家,我是工程師。我對那些四處遊蕩、望著雲端的人沒有任何意見。但是我是看著地面的人,我想修補就在我面前的坑洞,以免跌進去。」
- 從刪除 linked-list node 看程式設計的品味
- CMU Linked Lists
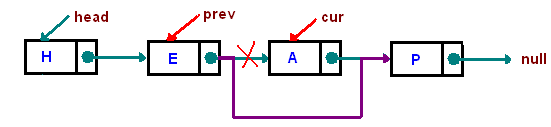
- 3 exceptional cases, we need to take care of:
- list is empty
- delete the head node
- node is not in the list
- CMU Linked Lists
- 原本的程式碼 (10 行)
void remove_list_node(List *list, Node *target)
{
Node *prev = NULL;
Node *current = list->head;
// Walk the list
while (current != target) {
prev = current;
current = current->next;
}
// Remove the target by updating the head or the previous node.
if (!prev)
list->head = target->next;
else
prev->next = target->next;
}
- 有「品味」的版本 (4 行)
void remove_list_node(List *list, Node *target)
{
// The "indirect" pointer points to the *address*
// of the thing we'll update.
Node **indirect = &list->head;
// Walk the list, looking for the thing that
// points to the node we want to remove.
while (*indirect != target)
indirect = &(*indirect)->next;
*indirect = target->next;
}
:::info 從「要更新什麼位置的資料」思考,無論是 head 或者非 head,更新的是同一類型的資料,不用特別操作,自然省下額外的處理 :::
延伸閱讀: Applying the Linus Torvalds "Good Taste" Coding Requirement
資料封裝
- dlist: Type-safe single file linked list
- dlist 使用方式
#include <dlist.h>
struct my_data { int data; }
dlist_declare(struct my_data, my_data);
void operate_on_data_list(dlist(my_data) *l) { ... }
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
dlist(my_data) *data = dlist_new(my_data);
}
circular linked list
用 龜兔賽跑(Floyd's algorithm)來偵測是否有 cycle 產生
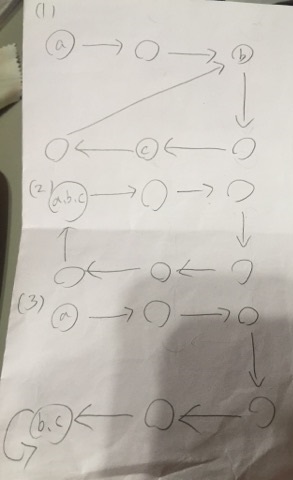
有 3 種狀態需要做討論
圖(1) cycle 在中間、圖(2) 頭尾相連、圖(3)為尾尾相連
- $a$ 為起始點
- $b$ 為連接點
- $c$ 為龜兔相遇位置
我們需要求得三點位置,才能進行處理 假設 $\overline{ac}$ 距離為 $X$ ,這代表 tortoise 走了 $X$ 步,那麼 hare 走了 $2X$ 步, $X$ 數值為多少並不重要,他只代表要花多少時間兩點才會相遇,不影響求出 $\mu , \lambda$ 接下來要分成三個步驟來處理
- step1: tortoise 速度為每次一步,hare 為每次兩步,兩者同時從起點 $a$ 出發,相遇時可以得到點 $c$。如果是圖(2)的狀況,在第一步結束就求完三點了
- step2: 兩點分別從點 $a$ 、 $c$ 出發,速度皆為一次一步,相遇時可以得到點 $b$。因為 $\overline{ac}$ 長度為 $X$,那麼 $cycle$ $c$ 長度也為 $X$,相遇在點 $b$ 時,所走的距離剛好都是 $X - \overline{bc}$
- step3: 從點 $b$ 出發,速度為一次一步,再次回到點 $b$ 可以得到 cycle 的長度
- cycle finding
如果只需要判斷是否為 circular linked list,那麼只要執行 step1 的部分,是很簡單。
除了計算 $\mu , \lambda$ ,還需要記錄整個串列的長度,若不記錄,會影響到之後 bubble sort 的實作。
Node *move(Node *cur) {
if (cur)
retunr cur->next;
return NULL;
}
bool cycle_finding(Node *HEAD, Node **TAIL, int *length, int *mu, int *lambda)
{
// lambda is length
// mu is the meet node's index
Node *tortoise = HEAD;
Node *hare = HEAD;
// get meet point
tortoise = move(tortoise);
hare = move(move(hare));
while (hare && tortoise) {
tortoise = move(tortoise);
hare = move(move(hare));
}
// not loop
if (!hare) {
*TAIL = NULL;
*length = 0;
tortoise = HEAD;
while(tortoise && (tortoise = move(tortoise))) {
(*length)++;
}
return false;
}
// get mu
*mu = 0;
tortoise = HEAD;
while (tortoise != hare) {
(*mu)++;
tortoise = tortoise->next;
hare = hare->next;
}
// get lambda
*lambda = 1;
tortoise = move(tortoise);
*TAIL = tortoise;
while (tortoise != hare) {
*TAIL = tortoise;
(*lambda)++;
tortoise = move(tortoise);
}
*length = *mu + *lambda;
return true;
}
開放原始碼專案中的實作
- Linux 核心
- include/linux/list.h
- 《Linux Device Drivers 3/e》, ch11.5 特點
- doubly linked list, circular
- API操作對象為struct list_head, 使用者需自行管理記憶體
- non thread-safe
- glib GList
- Doubly-Linked Lists, glib docs
- glist source
特點
- doubly linked list
- API操作對象為pointer to entry data (as void*), glib內部以
struct Glist表示節點, 用法較接近C++ std::list
struct _GList {
gpointer data;
GList *next;
GList *prev;
};
- 記憶體管理: GNOME memory slice
- 延伸資料結構: GQueue, GAsyncQueue, ...
- glib GQueue
glib GAsyncQueue
特點
- reference counting (g_async_queue_ref() and g_async_queue_unref())
- thread-safe: 以GAsyncQueue::mutex保護, 同一時間只有一個thread可變更queue
- 可自行管理lock (g_async_queue_lock() and g_async_queue_xxx_unlock())
API
// create
GAsyncQueue * g_async_queue_new ()
GAsyncQueue * g_async_queue_new_full ()
// operations
void g_async_queue_push ()
void g_async_queue_push_front ()
void g_async_queue_push_sorted () // the queue should be sorted
gpointer g_async_queue_pop () // blocking
gpointer g_async_queue_try_pop () // non-blocking
gpointer g_async_queue_timed_pop ()
gpointer g_async_queue_timeout_pop () // non-blocking
gboolean g_async_queue_remove ()
void g_async_queue_sort ()
gint g_async_queue_length ()
// reference counting
GAsyncQueue * g_async_queue_ref ()
void g_async_queue_unref ()
void g_async_queue_ref_unlocked ()
void g_async_queue_unref_and_unlock ()
// operations for manual lock/unlock
void g_async_queue_lock ()
void g_async_queue_unlock ()
void g_async_queue_push_unlocked ()
void g_async_queue_push_front_unlocked ()
void g_async_queue_push_sorted_unlocked ()
gpointer g_async_queue_pop_unlocked ()
gpointer g_async_queue_try_pop_unlocked ()
gpointer g_async_queue_timed_pop_unlocked ()
gpointer g_async_queue_timeout_pop_unlocked ()
gboolean g_async_queue_remove_unlocked ()
void g_async_queue_sort_unlocked ()
gint g_async_queue_length_unlocked ()
Linux 核心原始程式碼的實作
- Linux Kernel: 強大又好用的list_head結構
- Linux 核心鏈結串列
- 在 作業系統概念和文藝復興 線上講座的「從無到有打造 IoT 作業系統核心:以 Piko/RT 為例」提及 Piko/RT,仿效 Linux 核心原始程式碼的經典設計,也包含了 linked list
多執行緒和多核心的考量點
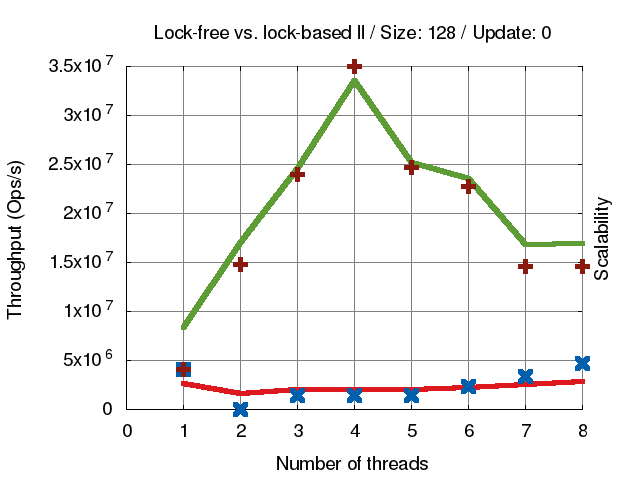
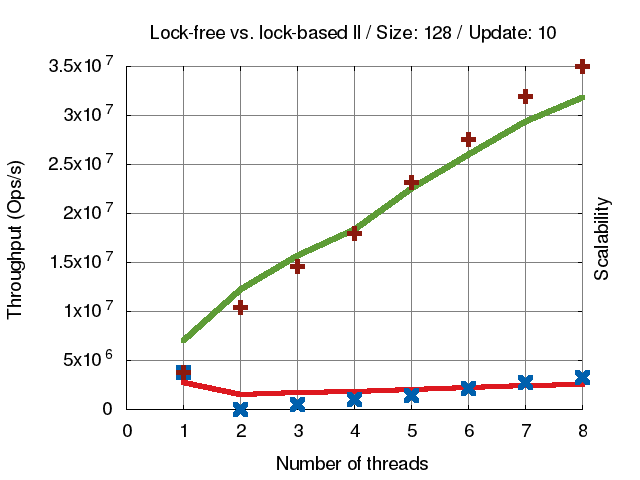
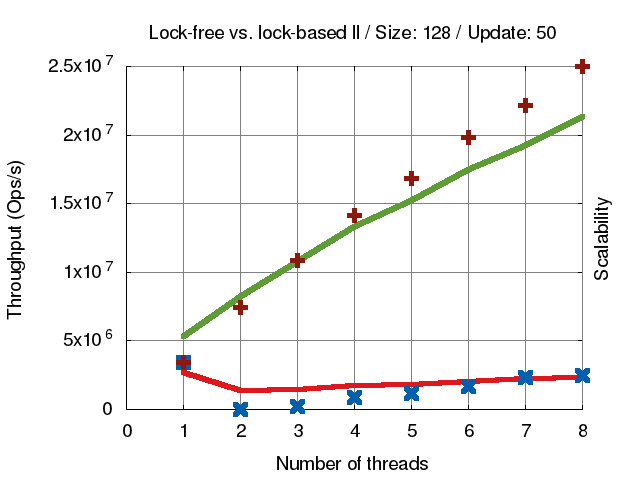
concurrent-ll程式碼,分析 lock和lock-free版本
十字叉叉代表 scalability(延伸擴展性) 線條代表 Throughput (資料吞吐量),綠色線條為lock-free,紅色線條為lock-based。可以很清楚看到 lock-based 的效能不管多少 thread 都不太會提升效能,而lock-free就會隨著 thread 變多效能提高。
- Throughput (吞吐量)
- Throughput is a measure of how many units of information a system can process in a given amount of time.
在單位時間內可以處理多少的資料量
- Scalability (擴展性)
- Scalability is the capability of a system, network, or process to handle a growing amount of work, or its potential to be enlarged in order to accommodate that growth.
可以處理越來越多的資料或工作時的能力或潛力
延伸閱讀: mergesort-concurrent